This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 471; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or re-approval.
Scope
1.1 This test method covers the required procedures to evaluate the comparative ability of rubber and rubber-like compositions to withstand the effect of liquids. It is designed for testing: (1) specimens of vulcanized rubber cut from standard sheets (see Practice D 3182), (2) specimens cut from fabric coated with vulcanized rubber (see Test Methods D 751), or (3) finished articles of commerce (see Practice D 3183). This test method is not applicable to the testing of cellular rubbers, porous compositions, and compressed sheet packing, except as described in 11.2.2.
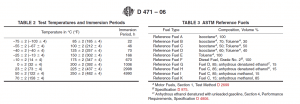
1.2 ASTM Oils No. 2 and No. 3, formerly used in this test method as standard test liquids, are no longer commercially available and in 1993 were replaced with IRM 902 and IRM 903, respectively (see Appendix X1 for details).
1.3 ASTM No. 1 Oil, previously used in this test method as a standard test liquid, is no longer commercially available and in 2005 was replaced with IRM 901; refer to Table 1, Footnote A, and Appendix X3 for details.
1.4 This test method includes the following: Change in Mass (after immersion) Section 10 Change in Volume (after immersion) Section 11 Dimensional-Change Method for Water-Insoluble Liquids and Mixed Liquids Section 12 Change in Mass with Liquid on One Surface Only Section 13 Determining Mass of Soluble Matter Extracted by the Liquid Section 14 Change in Tensile Strength, Elongation and Hardness (after immersion) Section 15 Change in Breaking Resistance, Burst Strength, Tear Strength and Adhesion for Coated Fabrics Section 16 Calculation (of test results) Section 17
1.5 The values stated in SI units are to be regarded as the standard. The values in parentheses are for information only.
1.6 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety and health practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Significance and Use
4.1 Certain rubber articles, for example, seals, gaskets, hoses, diaphragms, and sleeves, may be exposed to oils, greases, fuels, and other fluids during service. The exposure may be continuous or intermittent and may occur over wide temperature ranges.
4.2 Properties of rubber articles deteriorate during exposure to these liquids, affecting the performance of the rubber part, which can result in partial failure.
4.3 This test method attempts to simulate service conditions through controlled accelerated testing, but may not give any direct correlation with actual part performance, since service conditions vary too widely. It yields comparative data on which to base judgment as to expected service quality.
4.4 This test method is suitable for specification compliance testing, quality control, referee purposes, and research and development work.
ASTM D471-06 details the standardized method of this specification, please contact our engineers or ASTM directly at : https://www.astm.org/Standards/D471
Have a question? Please fill out the form below to receive information regarding your inquiry. You may also give us a call at (626) 965-9966.
Error: Contact form not found.